Unlimited availability of our money and its ability to be used as a medium of exchange create certainty and lead to personal freedom. But which payment method is proving to be the most robust in any crisis? A reflection on the value of cash in a free society.
By Jochen Werne, Management Board member, Chief Development & Chief Visionary Officer (CDO/CVO) of Prosegur Cash Services Germany GmbH
In times when our life is being affected significantly by the effects of the situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, we become more aware of the basic needs in our lives. However, the COVID-19 crisis, which hits us globally so hard that we are even prepared to give up some of our civil rights and liberties guaranteed by the constitution, also reveals what certainty means and gives us and what we rely on in order to overcome a crisis and regain our freedom.
We live in a world of exponential leaps in technology – and the technological progress has traditionally always resulted in a global improvement in living standards. The international community can be rightly proud of its achievement of reducing the percentage of people who have to live in absolute poverty from 35% to 8% in the last 30 years thanks to global trade. However, it is in times of crisis that we see just how sustainable the goals that have been achieved are. Here prudent and decisive action from political and business leaders is called for. Confidence gained in people and instruments is the greatest asset in times of uncertainty.
Cash: always available
The same applies for payments. While the independent good work over decades of many central banks such as the Deutsche Bundesbank, the European Central Bank and the US Federal Reserve is making itself noticeable in the crisis and the citizens rely on the stability of the euro and US dollar, cash is also showing itself to be an anchor of confidence in uncertain times. With growing concerns due to the coronavirus, in the USA for example the volume of physical cash in circulation has increased. In the week before 25 March this increased by 1.8% to 1.86 trillion dollars in absolute figures. This represents the biggest weekly increase since December 1999, when the fear of the so-called Millennium Bug was the reason for the rise. As we see today, the technological meltdown did not happen. However, 20 years later we are now more aware than ever of the vulnerability of technology and that in times of crisis the value of certainty is always the greatest asset. The increase in demand for cash, including in Germany, at the start of the corona crisis is probably attributable to this legitimate need of citizens for certainty and their great confidence in cash. According to the Bundesbank, the volume on Monday 16 March alone, the first day upon which schools and nurseries were closed, was 0.7 billion euros above the average.
Electronic payment methods, which are essential in so many areas such as online trading for example, repeatedly risk a loss of confidence due to technical failures. One of the most recent of these incidents occurred during of all times the Christmas shopping period on 23 December 2019, when EC card payments were no longer accepted at many terminals. It is a little like the situation described by the Roman poet Ovid: “People are slow to claim confidence in undertakings of magnitude.” Most certainly our savings – the fruit of our labour – are of this magnitude for us. It is for this reason that the availability of our money is so important. If this availability were restricted, we would start to feel that we might no longer be able to access our money, and a bank run would most likely be the result.
It is not without reason that the “supply of cash” is expressly defined as a “critical service” in Section 7 of the Regulation on the Identification of Critical Infrastructures (BSI-Kritisverordnung – BSI-KritisV) of the Federal Office for Information Security (BSI). That is to say a “service to supply the general public […], the loss or impairment of which would result in significant supply shortages or risks to public security.”
Certainty in uncertain times
In the COVID-19 crisis, anxiety about health and the economic consequences of any crisis dominate our daily life. While fear is clearly caused by an external threat, anxiety is indeterminate. As the Greek stoic philosopher Epictetus wrote in his Enchiridion of stoic morals: “People are not disturbed by things, but by the view they take of them.”
It was therefore also absolutely consistent that the World Health Organization (WHO), the European Central Bank, the Bundesbank and the Robert Koch Institute have been stressing repeatedly in the corona crisis that there is no documented case that would suggest there would be an increased virus risk due to the use of cash as opposed to card payment. They refer here to corresponding scientific studies and underline repeatedly that no information on such a risk has been documented.
Freedom established by the constitution
John Stuart Mill, one of the most successful liberal thinkers of the 19th century, defined freedom as the “first and strongest desire of human nature.” Accordingly, all governmental and social action must be directed towards granting the individual free development, while his freedom, as Mill formulates it in a principle known as the “principle of freedom,” may be limited under one condition: to protect himself or another person. Now, during a serious crisis, all citizens are forgoing some of their fundamental constitutional rights of freedom. This massive intervention is certainly consistent with Mills’ theory in this time of corona. In his novel The House of the Dead, Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky describes his own experiences of life in a Siberian prison camp and writes the subsequently oft-quoted sentence: “Money is coined liberty,” whereby he describes the vital relevance of a free exchange of goods in an environment where people are deprived of freedom – with cash in the form of coins.
Although not in the same way as Dostoevsky, we are also living in a time of extreme change: on a social, economic and political level. We are living in a time when, due to exponential technological developments, whole industries and business models are changing radically and countries are competing for supremacy in areas such as Artificial Intelligence (AI). It is a time in which transformation is the new norm and an agile corporate culture has to be the key to success. It is currently the case in many traditional industries that “anything that can be digitised, will be digitised.”
And inevitably this also raises the question of whether this is also the case for the first “instant payment” solution, one of the earliest and longest-lasting achievements of human civilisation – for our cash?
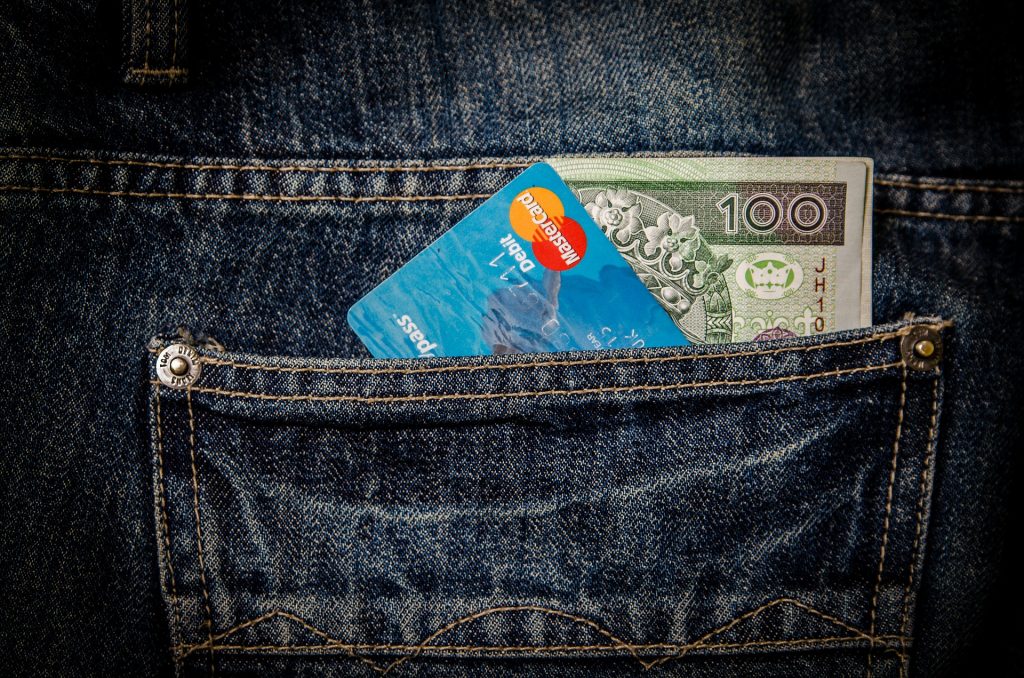
Our current free choice of payment method is certainly good, as long as we can choose freely as consumers the payment method appropriate for the respective situation. Discussions about the possible restriction of the freedom of choice of citizens regularly prompt intellectuals to issue warnings. For example, the poet Hans Magnus Enzensberger is of the opinion regarding the issue of “restriction”: “Those who abolish cash, abolish freedom.” This opinion is also shared by Carl-Ludwig Thiele, a former member of the Executive Board of the Deutsche Bundesbank: “Abolishing cash would hurt consumer sovereignty — the free choice of citizens about their payment instruments […] Government agencies do not have the right to tell citizens how they should pay.“
Technological vulnerability, fall-back option and data protection
Particularly in extreme scenarios such as disasters, failures of a digital infrastructure due to cyber attacks, natural events or simply due to technical failure, it is made clear that cash, by its nature, is currently the most robust payment method. The fact that the contactless payment limit has been increased without further ado, for example in supermarkets, at first sounds harmless. However, as a result, anyone can pay for higher-priced goods using a card, and it does not have to be their own card, without any further security checks such as entering a PIN. Everyone has to examine and question critically for themselves the possible consequences of such a payment method.
Also not to be disregarded is the issue of data protection. More cashless payments also mean more personal information disclosed by everyone. Data which numerous companies use for commercial purposes. At the latest since the introduction of the EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR), the sensitivity of the population of Europe with regard to data protection and privacy has been rising gradually.
Klaus Müller, Germany’s top consumer protector and Executive Director of the Federation of German Consumer Organisations (vzbv), describes cash as “data protection in practice”. Anyone who pays with cash does not leave any traces to create a consumer profile, purchasing and payment behaviour cannot be manipulated. Cash also helps to protect financial privacy. This was emphasised by Udo Di Fabio, who was a judge of the Federal Constitutional Court for twelve years, at the Cash Symposium 2018 hosted by Deutsche Bundesbank. He explained that every citizen can dispose freely of their money. In his view this freedom would be restricted if financial management were completely digitised.
Smart cash management alleviates the workload of banks
Crises such as the current corona pandemic always bring to light new approaches and act as accelerators of transformation processes that have already been set in motion. With regard to cash-related industries, the banking world has already been in a transformation process for some time. A company such as Prosegur, which, with over 4,000 employees and 31 branches, is a market leader in Germany in the transportation of cash and valuables, is increasingly becoming a full payment-platform provider. Several banks have already taken the path of fully outsourcing their cash management for synergy and cost-saving reasons. Here, cash processes are becoming not only much leaner, but also more cost-effective. This is the case not only for banks, but also for retail customers. With smart machines installed by Prosegur at its customers, cash can be disposed of directly and credited to the customer account on the same day. The smart infrastructure, including dynamic monitoring and forecasting, optimises the logistics and reduces costs in cash logistics. This is the next step towards an efficient, digital and integrated cash management.
Coined Liberty 2.0 and the justification for and rightfulness of cash
In view of the technological progress and the associated social changes, it can be seen that key values from the human perspective are still valid. Based on an intellectual, serious discussion, the relevance to today of the theories of for example Dostoevsky with his experiences in an unfree society is clear: The discussion about the civil rights and liberties of citizens is always very closely related to their ability to use cash freely, to their freedom of choice of payment method and ultimately to the rightfulness of their actions with regards also to effiency and impact.
Our open and liberal society is characterised by the fact that we are discussing and most certainly will continue to discuss “Coined Liberty 2.0” at this level.
Prosegur Cash Services Germany GmbH, Kokkolastraße 5, 40882 Ratingen
Telephone: +49 2102 / 1248‐0, E‐mail: redaktion@prosegur.com, www.prosegur.de