It is an honour to be able to support this forward-looking Data Literacy Charter, initiated by the Stifterverband, as a first signatory together with the most competent representatives from politics, education, business and science.
Jochen Werne
DATA LITERACY CHARTA
Find all original information in German > HERE / please find below a translation for English speaking audience – created with DeepL.com
 The Data Literacy Charter, initiated by the Stifterverband in January 2021 and supported by numerous professional societies, formulates a common understanding of data literacy and its importance for educational processes. The charter is in line with the Federal Government’s data strategy and with the Berlin Declaration on the Digital Society.
The Data Literacy Charter, initiated by the Stifterverband in January 2021 and supported by numerous professional societies, formulates a common understanding of data literacy and its importance for educational processes. The charter is in line with the Federal Government’s data strategy and with the Berlin Declaration on the Digital Society.
Author and authors:
Katharina Schüller, Henning Koch, Florian Rampelt
SUMMARY
Data literacy encompasses the data skills that are important for all people in a world shaped by digitalisation. It is an indispensable part of general education.
 With the Data Literacy Charter, the signatories express the common understanding of data literacy in the sense of comprehensive data literacy and its importance in educational processes. This understanding is in line with the Federal Government’s data strategy and with the Berlin Declaration on the Digital Society.
With the Data Literacy Charter, the signatories express the common understanding of data literacy in the sense of comprehensive data literacy and its importance in educational processes. This understanding is in line with the Federal Government’s data strategy and with the Berlin Declaration on the Digital Society.
Data literacy includes the skills to collect, manage, evaluate and apply data in a critical way. If data is to support decision-making processes, it needs competent answers to four fundamental questions:
What do I want to do with data? Data and data analysis are not an end in themselves, but serve a concrete application in the real world.
What can I do with data? Data sources and their quality as well as the state of technical and methodological developments open up possibilities and set limits.
What am I allowed to do with data? All legal rules of data use (e.g. data protection, copyrights and licensing issues) must always be considered.
What should I do with data? Because data is a valuable resource, a normative claim derives from it to use it for the benefit of individuals and society.
The supporters of the Charter see data literacy as a central competence of all people in the 21st century. It is the key to systematically transforming data into knowledge.
Data literacy enables people, businesses and scientific institutions, as well as governmental or civil society organisations,
to actively participate in the opportunities offered by data use;
deal confidently and responsibly with their own and other people’s data;
to use new drivers and technologies such as Big Data, Artificial Intelligence or Internet of Things to meet individual needs, address societal challenges and solve global problems.
Data literacy strengthens judgement, self-determination and a sense of responsibility and promotes the social and economic participation of all of us in a world shaped by digitalisation.
GUIDING PRINCIPLES
Five principles characterise the importance and role of data literacy as a key competence of the 21st century.
Data literacy must be accessible to all.
Data literacy serves to promote maturity in a modern digitalised world and is therefore important for all people – not only for specialists. The aim of teaching data literacy is to ensure that each individual and our society as a whole deal with data in a conscious and ethically sound manner. Data literacy enables successful and sustainable action that is based on evidence and that takes appropriate account of uncertainty and change in our living environment. We are therefore committed to ensuring that data literacy is taught broadly and can be acquired by all people.
Data literacy must be taught throughout life in all areas of education.
Data literacy must be anchored in all formal and non-formal education sectors and thus established as part of general education. To do this, we must continuously teach learners how data relates to their respective lifeworlds: Data are digital images of real phenomena, objects and processes – this applies to all fields of application. How to collect or procure, evaluate, apply and interpret data appropriately for the respective application must be systematically learned and practised. The basic concept of data literacy and its sub-areas therefore applies across the board, even if the level of competence imparted varies depending on the educational sector and level.
In concrete terms, this requires the inclusion of data literacy in the curricula and educational standards of schools, in the curricula of degree programmes and in teacher training programmes. Learners should not only be addressed as passive consumers of data. Rather, we want to enable them to actively shape data-related knowledge and decision-making. In order to make lifelong learning of data literacy possible, data literacy programmes for extracurricular and vocational training are also needed. We advocate developing and promoting these, for example, together with adult education centres or public libraries.
Data literacy must be taught as a transdisciplinary competence from three perspectives.
Data literacy involves three perspectives: the application-related (“What is to be done?”), the technical-methodical (“How is it to be done?”) and the social-cultural (“What is it to be done for?”). We therefore want to ensure that data literacy is taught from a trans- and interdisciplinary approach. This includes
● the application-oriented perspective (for example, applications from the natural and engineering sciences, economics, medicine, psychology, sociology, linguistics, media studies and many more),
the technical-methodological perspective (for example, from the perspective of statistics, mathematics, computer science and information science),
the socio-cultural perspective (for example, reflection on legal, ethnological, ethical, philosophical as well as inequality aspects)
● as well as the perspective of teaching (for example on the part of subject didactics and educational science).
Data literacy must systematically cover the entire process of knowledge and decision-making with data.
Data literacy ensures that answers to real problems are found with the help of data in a structured and qualitative way. Data literacy therefore includes the following areas of competence:
● Using and protecting data (ability and motivation to responsibly acquire, analyse, share and obtain appropriate data and information in the context of the task at hand).
Classify data and information derived from it (ability and motivation to contextualise and interpret data and information and to critically question learning systems, such as AI applications).
● Act in a data-supported manner (open-minded attitude towards data in the sense of a data culture including insight into the role of data for evidence-based action, ability to handle data with confidence including effective communication of data-based decisions).
Data literacy must comprise knowledge, skills and values for a conscious and ethically sound handling of data.
Data literacy comprises three competence dimensions that must be mapped in all three competence areas. Each competence area is characterised by
● specific knowledge (dimension “Knowledge”),
● the skills and abilities to apply this knowledge (dimension “Skills”) and
● by the willingness to do so, i.e. the corresponding value attitude (dimension “Values”).
Data ethics is a central component of a key competence and is reflected in all sub-areas of data literacy. This means that when data is collected, managed, evaluated and used in a critical way, ethical aspects play an important role throughout. Data ethics and values contribute significantly to ensuring that not only the right means are used to solve problems with the help of data, but above all that the right goals are pursued: Data should make a sustainable positive contribution to society and therefore be used responsibly, context-sensitively and with a view to possible future consequences.
The signatories of the Data Literacy Charter will take measures to disseminate this understanding of data literacy and to further strengthen the associated competences. They call on other actors to do the same in their sphere of influence.
The initial signatories
Institutions & Initiatives (in alphabetical order)
- Bund Katholischer Unternehmer e.V. (BKU)
- Deutsche Arbeitsgemeinschaft Statistik (DAGStat) mit ihren 14 Mitgliedsgesellschaften und dem Statistischen Bundesamt Destatis
- Deutscher Volkshochschul-Verband (DVV)
- Deutsche Statistische Gesellschaft (DStatG)
- Digitalrat der Bundesregierung
- Europäisches Wirtschaftsforum e.V. – EWiF Deutschland
- Federation of European National Statistical Societies (FENStatS) mit ihren 27 Mitgliedsgesellschaften und der Europäischen Zentralbank
- FernUniversität in Hagen
- FOM Hochschule für Oekonomie & Management
- Hochschulforum Digitalisierung
- Initiative for Applied Artificial Intelligence by UnternehmerTUM
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), European Office
- International Association for Statistical Education (IASE)
- KI Bundesverband e.V.
- KI-Campus – Die Lernplattform für Künstliche Intelligenz
- Partnership in Statistics for the Development in the 21st Century (PARIS21) / OECD
- RWI – Leibniz-Institut für Wirtschaftsforschung
- Stifterverband
- Technische Universität Dortmund
- Weltethos-Institut | An-Institut der Universität Tübingen
Individuals (in alphabetical order)
Regina Ammicht Quinn, Dorothee Bär, Thomas K. Bauer, Manfred Bayer, Jörg Bienert, Felicitas Birkner, Vanessa Cann, Thomas M. Deserno, Roman Dumitrescu, Johanna Ebeling, Florian Ertz, Andrea Frank, Gerd Gigerenzer, Jessica Heesen, Ulrich Hemel, Norbert Henze, Burghard Hermeier, Wolfgang Heubisch, Oliver Janoschka, Johannes Jütting, Claudia Kirch, Volker Knittel, Henning Koch, Ralf Klinkenberg, Annegret Kramp-Karrenbauer, Alexander Knoth, Beate M. Kreiner, Sebastian Kuhn, Monique Lehky Hagen, Andreas Lenz, Andreas Liebl, Anna Masser, Volker Meyer-Guckel, Antje Michel, Ralf Münnich, Dominic Orr, Ada Pellert, Martin Rabanus, Walter J. Radermacher, Philipp Ramin, Florian Rampelt, Richard K. Frhr. v. Rheinbaben, Peter Rost, Philipp Schlunder, Harald Schöning, Katharina Schüller, Rainer Schwabe, Andrea Stich, Sascha Stowasser, Renata Suter, Georges-Simon Ulrich, Daniel Vorgrimler, Jochen Werne, Johannes Winter
The hallmark of an open society is that it promotes the unleashing of people’s critical faculties, and the Data Literacy Charter, in this best sense, promotes the much-needed creation of data literacy for all areas of our digital society
Jochen Werne














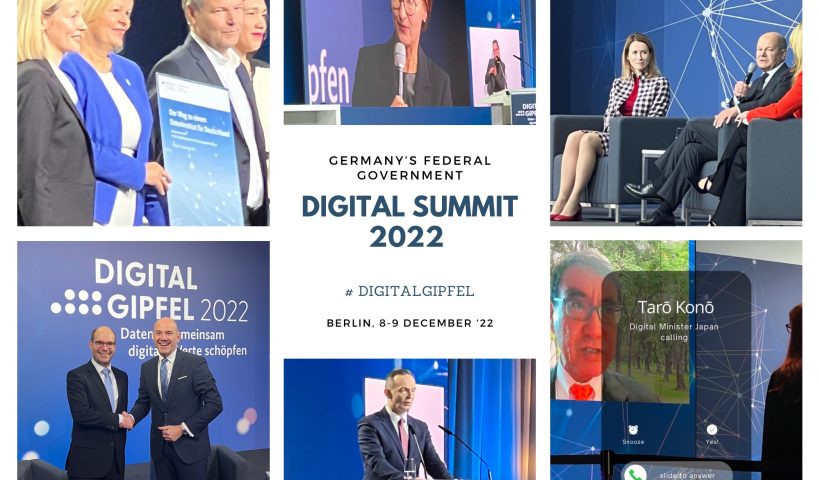























 The Data Literacy Charter, initiated by the Stifterverband in January 2021 and supported by numerous professional societies, formulates a common understanding of data literacy and its importance for educational processes. The charter is in line with the Federal Government’s data strategy and with the Berlin Declaration on the Digital Society.
The Data Literacy Charter, initiated by the Stifterverband in January 2021 and supported by numerous professional societies, formulates a common understanding of data literacy and its importance for educational processes. The charter is in line with the Federal Government’s data strategy and with the Berlin Declaration on the Digital Society. With the Data Literacy Charter, the signatories express the common understanding of data literacy in the sense of comprehensive data literacy and its importance in educational processes. This understanding is in line with the Federal Government’s data strategy and with the Berlin Declaration on the Digital Society.
With the Data Literacy Charter, the signatories express the common understanding of data literacy in the sense of comprehensive data literacy and its importance in educational processes. This understanding is in line with the Federal Government’s data strategy and with the Berlin Declaration on the Digital Society.